Table of Contents
1. Tensorflow中张量形状变换
tf.argmax
1.1. tf.math.reduce_sum
# 降维加和,比如一个数组是333大小的,那么经过这个操作之后会变为一个数字,即所有元素的加和。 tf.math.reduce_sum( input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None, keep_dims=None ) x = tf.constant([[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]]) # x.shape=(2,3) y=tf.reduce_sum(x) # 6标量 >>>type(y) tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Tensor y_result=sess.run(y) # 6标量 tf.reduce_sum(x, 0) # [2, 2, 2] y.shape=(3) tf.reduce_sum(x, 1) # [3, 3] y.shape=(2) tf.reduce_sum(x, 1, keepdims=True) # [[3], [3]] y.shape=(1,3) tf.reduce_sum(x, [0, 1]) # 6 y.shape=标量
1.1.1. tf.reduce_mean
tf.reduce_mean(Tensor):降维平均,和上面的reduce_sum一样,将高维的数组变为一个数,该数是数组中所有元素的均值。
1.1.2. tf.one_hot()
ndices表示输入的多个数值,通常是矩阵形式;depth表示输出的尺寸。
由于one-hot类型数据长度为depth位,其中只用一位数字表示原输入数据,这里的on_value就是这个数字,默认值为1,one-hot数据的其他位用off_value表示,默认值为0。
tf.one_hot()函数规定输入的元素indices从0开始,最大的元素值不能超过(depth - 1),因此能够表示depth个单位的输入。若输入的元素值超出范围,输出的编码均为 [0, 0 … 0, 0]。
indices = 0 对应的输出是[1, 0 … 0, 0], indices = 1 对应的输出是[0, 1 … 0, 0], 依次类推,最大可能值的输出是[0, 0 … 0, 1]。
代码示例如下:
y=tf.one_hot( indices, depth, on_value=None, off_value=None, axis=None, dtype=None, name=None ) tpye(y) >>>
labels = [0, 2, -1, 1] res = tf.one_hot(indices=labels, depth=4, on_value=1.0, off_value=0.0, axis=-1) b =sess.run(res) >>> b array([[1., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)
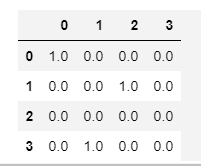
labels = [0, 2, -1, 1] res = tf.one_hot(indices=labels, depth=4, on_value=1.0, off_value=0.0, axis=1) b =sess.run(res) >>> b array([[1., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 1.], [0., 1., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)
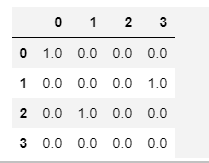
度变化情况为(2 * 2)->(2 * 2 * 4)。
reshape
reshape
2. 格式转换
字符串转为数字: tf.string_to_number(string_tensor, out_type=None, name=None) 转为64位浮点类型–float64: tf.to_double(x, name=’ToDouble’) 转为32位浮点类型–float32: tf.to_float(x, name=’ToFloat’) 转为32位整型–int32: tf.to_int32(x, name=’ToInt32’) 转为64位整型–int64: tf.to_int64(x, name=’ToInt64’) 将x或者x.values转换为dtype # tensor a is [1.8, 2.2], dtype=tf.float # tf.cast(a, tf.int32) ==> [1, 2],dtype=tf.int32 tf.cast(x, dtype, name=None)
